Exploring the role of digital assets in B2B cross-border payments

The digital asset space is vast, and it can it be easy to get lost in a sea of definitions and labels. But understanding the role that digital assets can play in improving the existing financial ecosystem and the payments space, in particular, is critical for businesses that want to operate on a global scale.
Demystifying Digital Assets
Think of 'digital assets' as a category of assets that includes anything minted and exchanged on a blockchain.
Blockchains are the technology solutions that enable digital assets. A blockchain is a method of securely recording information on a peer-to-peer network. It operates as a shared public database across multiple computer systems, in which anyone can add new entries but existing ones cannot be altered or deleted. Each blockchain entry, called 'blocks' contains specific information, about the previous block, reinforcing the structure and order of the chain as it grows.
Digital assets are created when new information is added to a particular blockchain. It is through blockchain entires that users can exchange existing digital assets or create new ones.
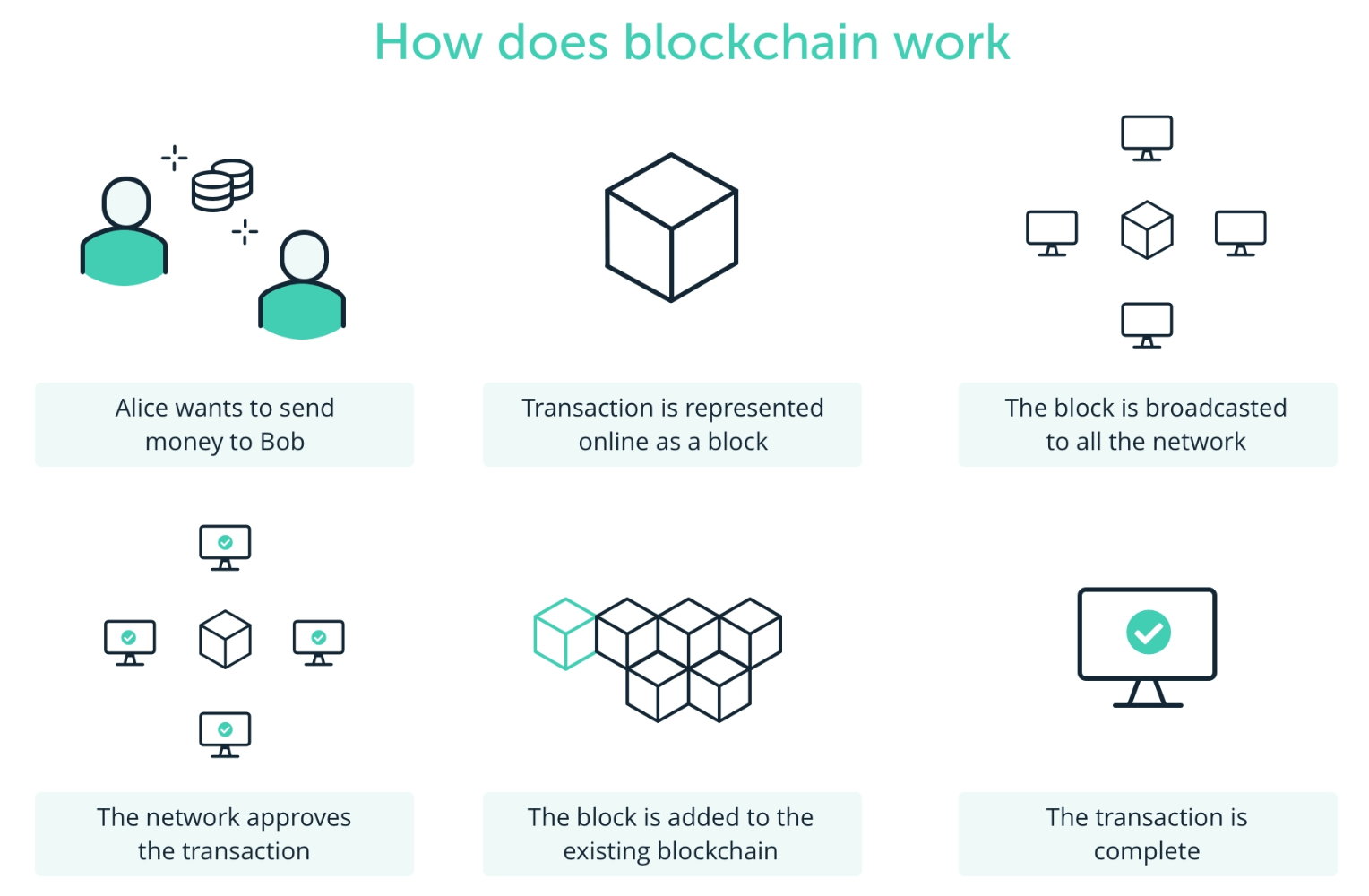
Source: Ledger
There are generally 5 categories of digital assets:
- Cryptocurrencies
- Stablecoins
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- Security tokens
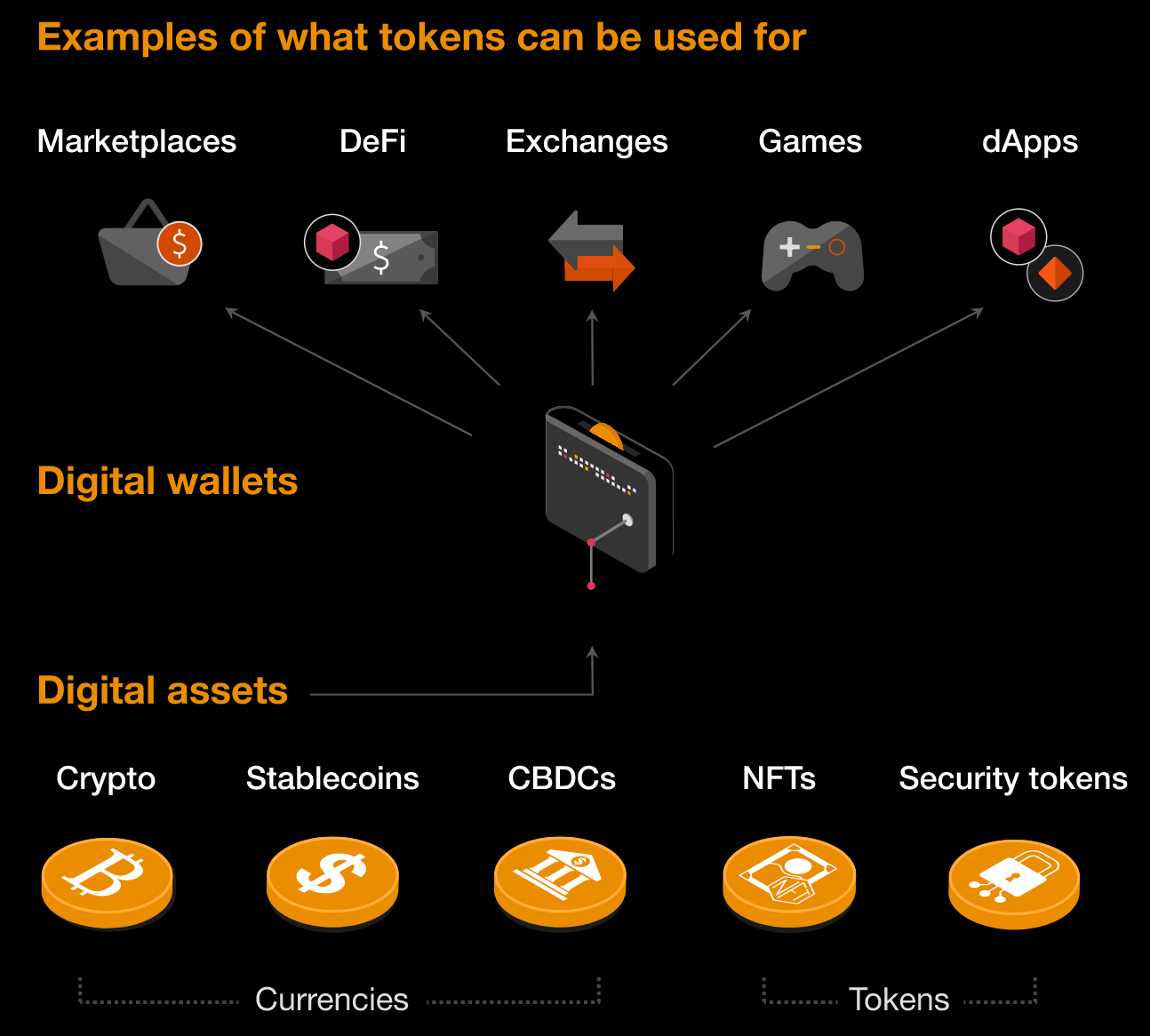
Source: PWC
The State of Digital Assets Today
Digital assets like cryptocurrencies, NFTs and other 'tokens' have gone mainstream.
Today, it is estimated that 220m people around the world own cryptocurrency, with user growth rates increasing a staggering 113% a year. Crypto transaction volumes are growing even faster, increasing 567% from 2021-2022. Central banks around the world including, India, Brazil, UK, Sweden and the US, are now developing their own variations of cryptocurrencies - known as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) - illustrating how blockchain technology and digital assets are fast becoming a staple of the payments ecosystem.
The opportunity for payments businesses who are ready to embrace this technology is significant. But what role do cryptocurrencies play in B2B cross-border payments?
Traditional Cross-Border Payments
Cross-border payments, also known as SWIFT payments or wire transfers, are international payments settled between banks that have a correspondent banking relationship. The global economy of cross-border payments cannot be understated. B2B cross-border payments alone are expected to be a $35 trillion economy by the end of 2022.
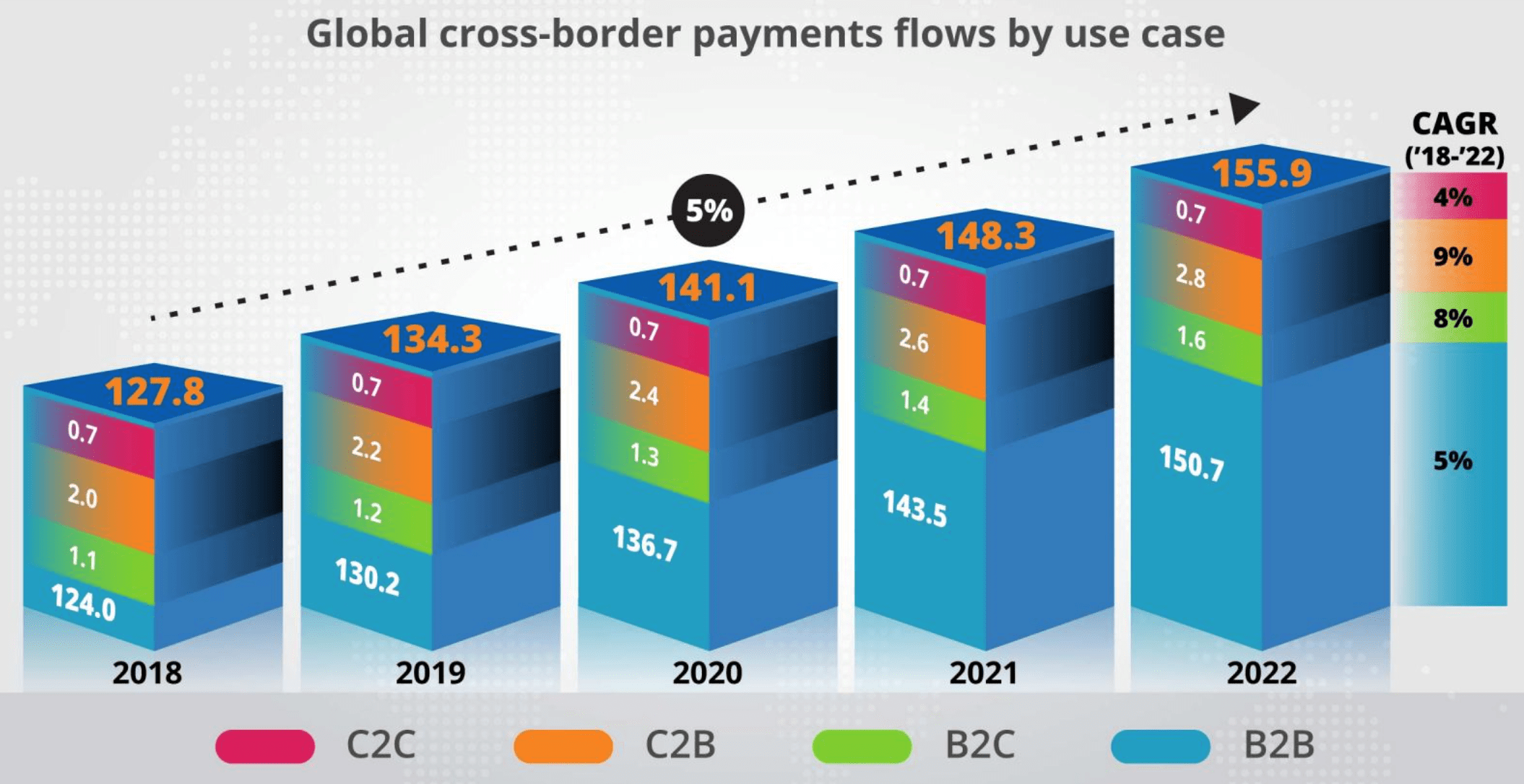
Source: Ernst & Young
In the traditional system, domestic banks generally facilitate cross-border payments, with banks in the correspondent banking network acting as intermediaries by collecting funds in the local currency from the sender, exchange the funds into a different currency, and then transferring those funds to the destination country bank. Costs can vary and could include an exchange rate margin (charge on top of the market exchange rate), correspondent banking fees as well as any transaction fees from the domestic bank initiating the transfer.
An example:
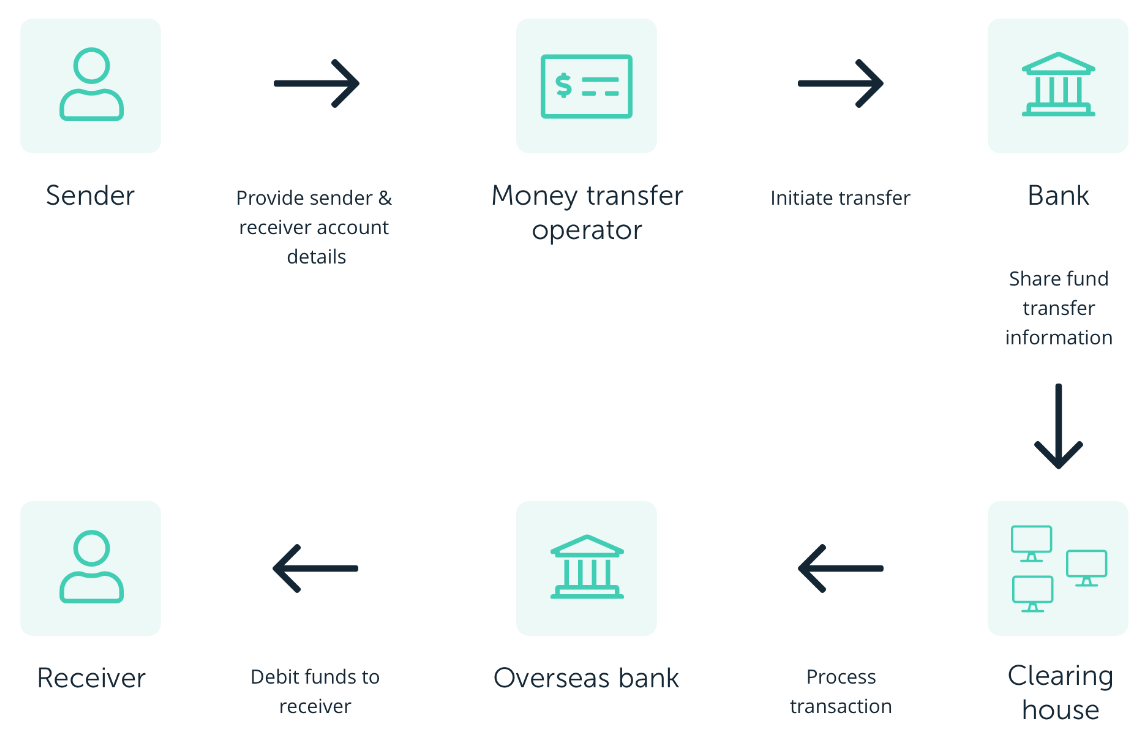
Source: Ledger
In this ecosystem, making payments between businesses, vendors and contractors around the world is difficult. That's because most cross-border payments involve:
- lengthy settlement times
- high transaction fees, and
- too many intermediaries
How Digital Assets Can Improve Cross-Border Payments
Digital currencies, when combined with blockchain technology, tackle a range of significant pain points for businesses making B2B cross-border payments:
Speed
Any blockchain-enabled cross-border payment has near instant processing and settlement times 24/7.
Cost
Cryptocurrencies are decentralised, since the blockchain allows users to transact without the need for a third-party (correspondent banks). Bypassing intermediaries and clearing houses reduces transaction costs by avoiding third-party fees.
Improved Data Transparency & Security
The blockchain network is a fully auditable and accurate ledger of transactions. While all transactions done on the network are recorded, they are also indelible, making the entire process of manipulating data impossible.
Institutional Adoption of Digital Assets is Growing
The institutional adoption of digital assets for payments is gaining momentum. In the US alone, 2,300 organisations like Paypal, Microsoft, Whole Foods and UNICEF have begun accepting cryptocurrency as a form of payment.

A 2022 New Value report from Ripple found that across financial institutions, 76% expect to use crypto in the next three years. Their report also found that there were widespread perceived benefits of of using crypto among this same group:
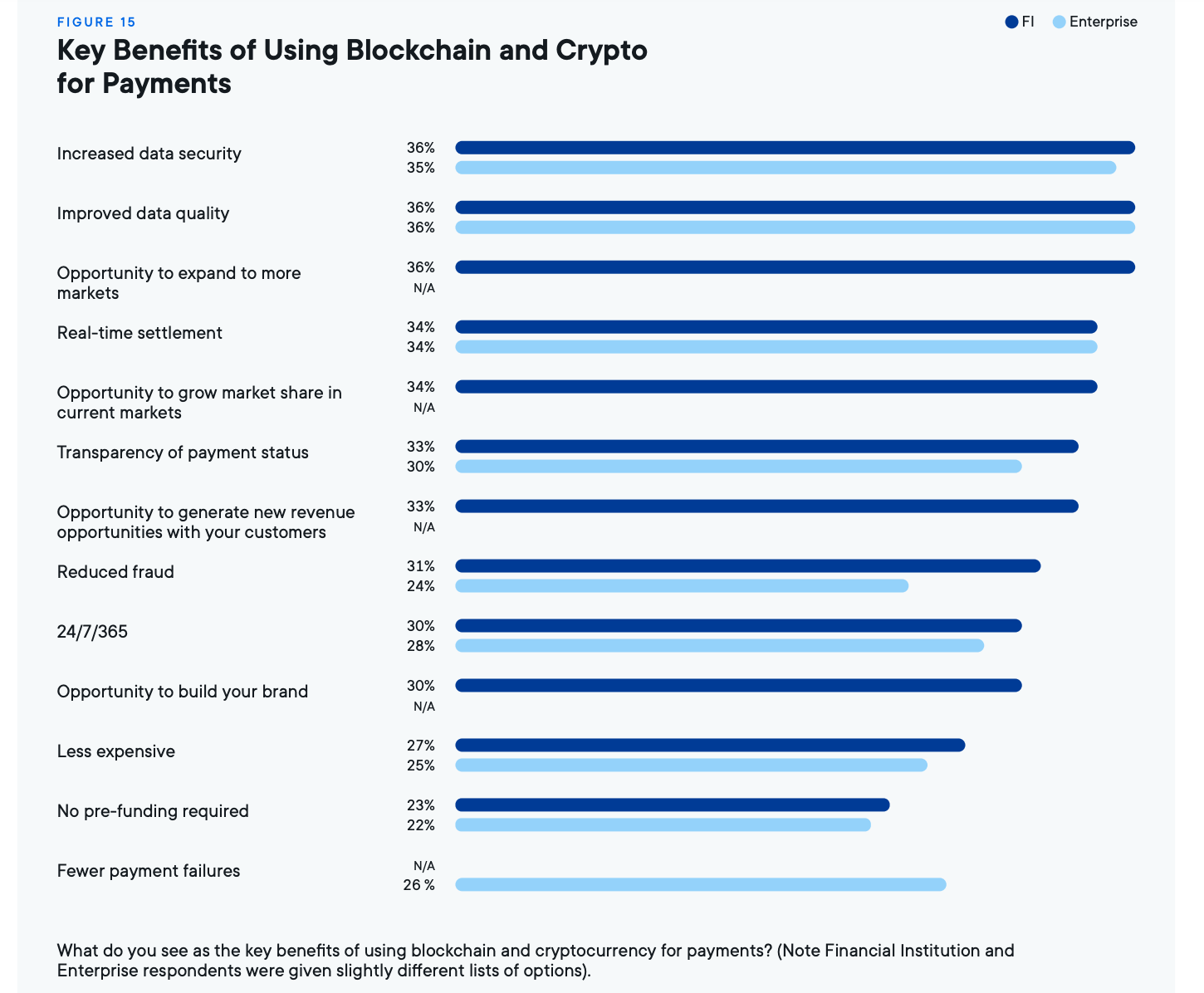
Ripple and XRP - a payments use case
Crypto can be used for payments in a way that is invisible to the individual, as when, for example, it acts as a bridge currency between fiat currencies.
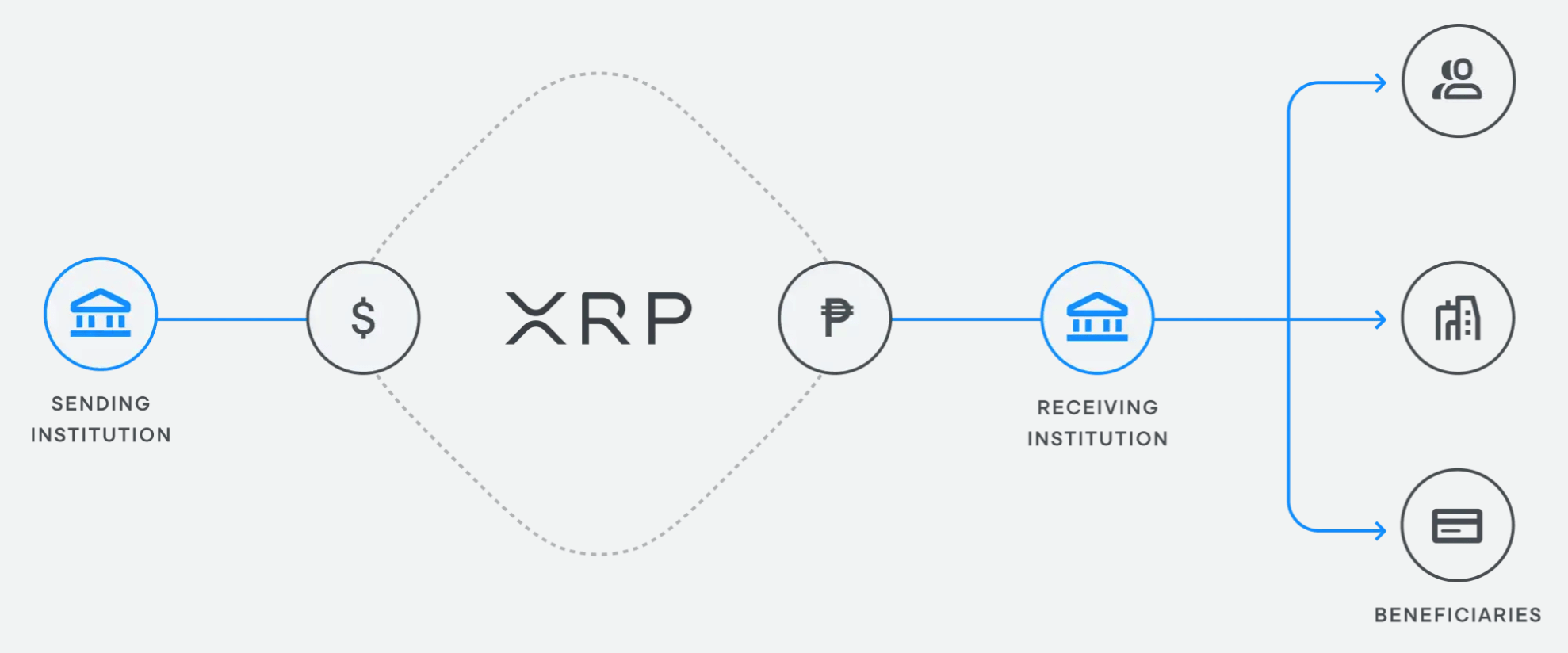
Ripple uses XRP - a digital asset native to the XRP ledger - to bridge two fiat currencies without going through the traditional intermediaries. The use of XRP eliminates pre-funding, reduces operational costs and unlocks capital to make exchange and settlement much easier and faster.
How Ripple's XRP solution for payments works:
Flash Payments has been at the forefront of using digital assets to improve legacy cross-border payments processes. As an early adopter of Ripple's On-Demand-Liquidity solution (which uses XRP as bridging currency), we strongly believe in the transformational power of digital assets in the area of international payments.

